UW Interactive Data Lab
papers

How Do Data Analysts Respond to AI Assistance? A Wizard-of-Oz Study
Ken Gu, Madeleine Grunde-McLaughlin, Andrew McNutt, Jeffrey Heer, Tim Althoff.
Proc. ACM Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), 2024
Proc. ACM Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI), 2024
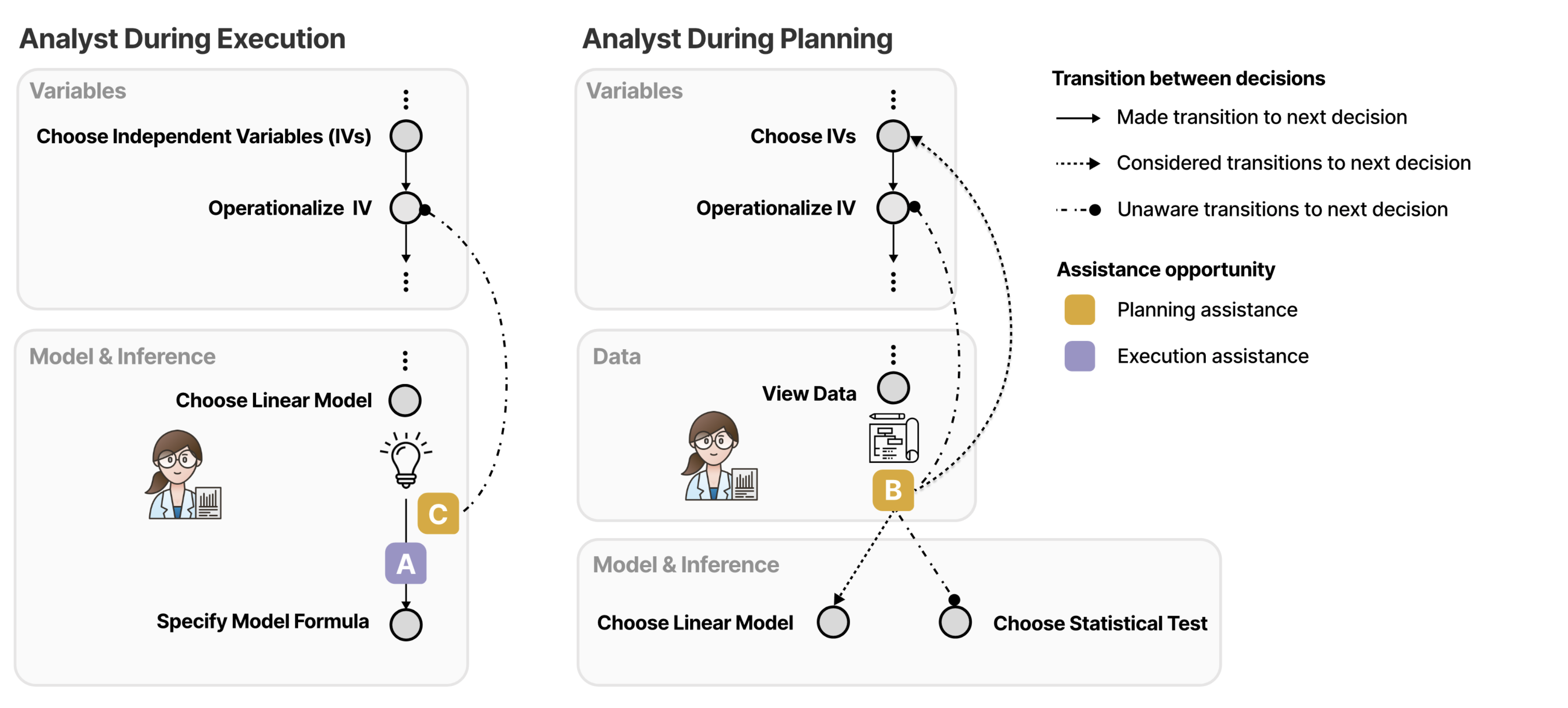
Materials
Abstract
Data analysis is challenging as analysts must navigate nuanced decisions that may yield divergent conclusions. AI assistants have the potential to support analysts in planning their analyses, enabling more robust decision making. Though AI-based assistants that target code execution (e.g., Github Copilot) have received significant attention, limited research addresses assistance for both analysis execution and planning. In this work, we characterize helpful planning suggestions and their impacts on analysts' workflows. We first review the analysis planning literature and crowd-sourced analysis studies to categorize suggestion content. We then conduct a Wizard-of-Oz study (n=13) to observe analysts' preferences and reactions to planning assistance in a realistic scenario. Our findings highlight subtleties in contextual factors that impact suggestion helpfulness, emphasizing design implications for supporting different abstractions of assistance, forms of initiative, increased engagement, and alignment of goals between analysts and assistants.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{2024-analyst-ai-woz,
title = {How Do Data Analysts Respond to AI Assistance? A Wizard-of-Oz Study},
author = {Gu, Ken AND Grunde-McLaughlin, Madeleine AND McNutt, Andrew AND Heer, Jeffrey AND Althoff, Tim},
booktitle = {Proc. ACM Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI)},
year = {2024},
url = {https://idl.uw.edu/papers/analyst-ai-woz},
doi = {10.48550/arXiv.2309.10108}
}
